
|
|
PDF NCP1835B Data sheet ( Hoja de datos )
| Número de pieza | NCP1835B | |
| Descripción | Integrated Li-Ion Charger | |
| Fabricantes | ON Semiconductor | |
| Logotipo | ||
Hay una vista previa y un enlace de descarga de NCP1835B (archivo pdf) en la parte inferior de esta página. Total 14 Páginas | ||
|
No Preview Available !
NCP1835B
Integrated Li−Ion Charger
NCP1835B is an integrated linear charger specifically designed to
charge 1−cell Li−Ion batteries with a constant current, constant
voltage (CCCV) profile.
Its low input voltage capability, adjustable charge current, ability
to maintain regulation without a battery, and its onboard thermal
foldback make it versatile enough to charge from a variety of wall
adapters. The NCP1835B can charge from a standard wall adapter or
from the USB port. It has been optimized to charge low capacity
batteries such as those found in wireless headsets and flash
memory−based MP3 players. It’s recommended charge current rate
is 30−300 mA.
Features
• Integrated Voltage and Current Regulation
• No External MOSFET, Sense Resistor or Blocking Diode Required
• Charge Current Thermal Foldback
• Integrated Pre−charge Current for Conditioning a Deeply
Discharged Battery
• Integrated End−of−Charge (EOC) Detection
• 1% Voltage Regulation
• 4.2 V Regulated Output Voltage
• Regulation Maintained without a Battery Present
• Programmable Full Charge Current
• Open−Drain Charger Status and Fault Alert Flags
• 2.8 V Output for AC Present Indication and Powering Charging
Subsystems
• Minimum Input Voltage of 2.4 V Allows Use of Current Limited
Adapters
• Automatically Recharging if Battery Voltage Drops after Charging
Cycle is Completed
• Low Profile 3x3 mm DFN Package
• Pb−Free Package is Available
Typical Applications
• Wireless Headsets
• MP3 Players
• USB Appliances
• Battery Operated Devices
www.DataSheet4U.com
http://onsemi.com
MARKING
DIAGRAM
1
DFN 3x3
MN SUFFIX
CASE 485C
1
1835B
ALYW
1835B = Device Code
A = Assembly Location
L = Wafer Lot
Y = Year
W = Work Week
PIN CONNECTIONS
VCC 1
FAULT 2
CFLG 3
TIMER 4
GND 5
DFN 3x3
10 BAT
9 VSNS
8 ISEL
7 V2P8
6 EN
(Top View)
ORDERING INFORMATION
Device
Package
Shipping†
NCP1835BMNR2 DFN−10 3000 Units/Reel
NCP1835BMNR2G DFN−10 3000 Units/Reel
(Pb−Free)
†For information on tape and reel specifications,
including part orientation and tape sizes, please
refer to our Tape and Reel Packaging Specification
Brochure, BRD8011/D.
© Semiconductor Components Industries, LLC, 2005
June, 2005 − Rev. 0
1
Publication Order Number:
NCP1835B/D
1 page 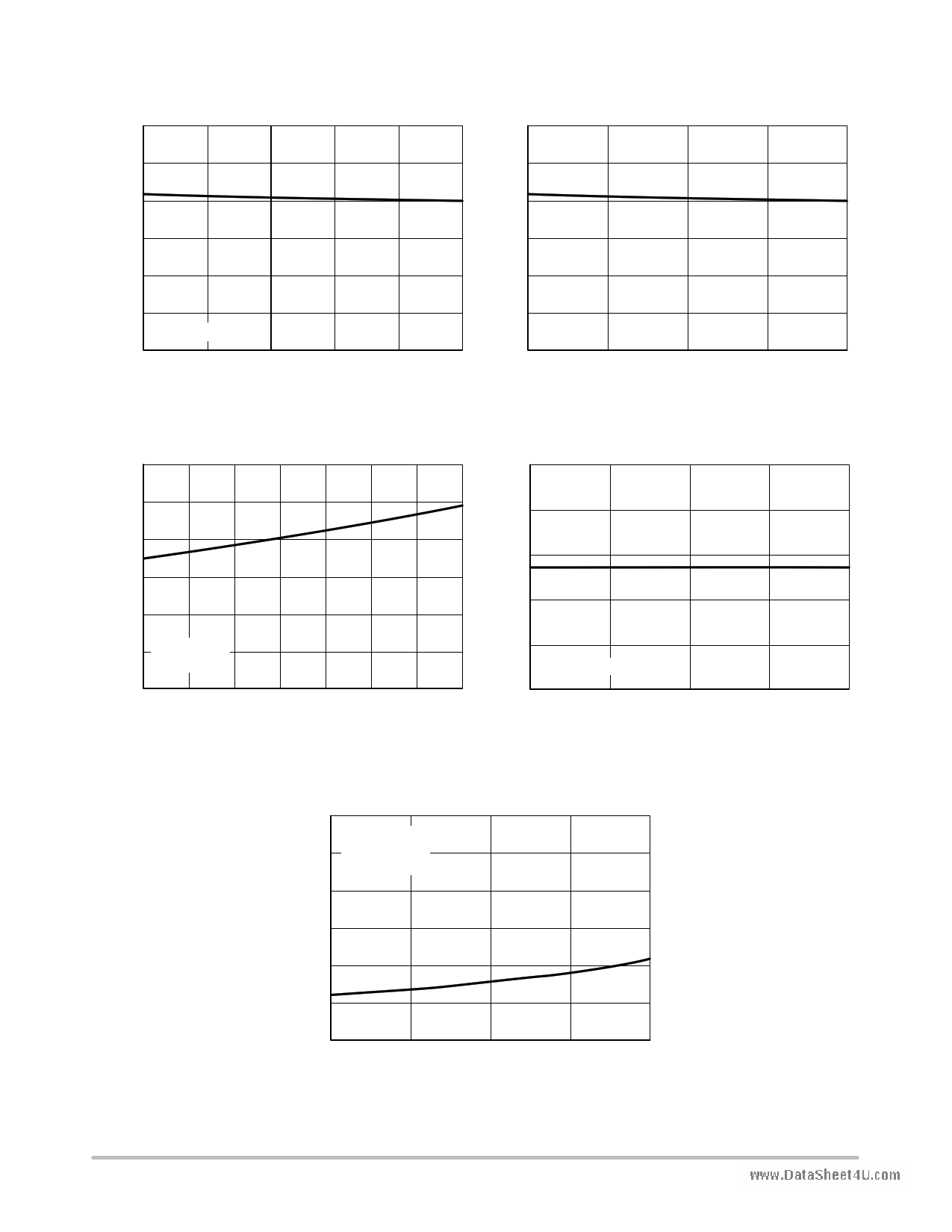
NCP1835B
TYPICAL OPERATING CHARACTERISTICS
www.DataSheet4U.com
4.30 4.30
4.25 4.25
4.20 4.20
4.15 4.15
4.10 4.10
4.05
VCC = 5 V
4.00
0
0.06
0.12
0.18
0.24
ICHG, CHARGE CURRENT (A)
0.3
Figure 2. Regulated Output Voltage vs. Charge
Current
4.05
4.00
4.5
5 5.5 6
VCC, INPUT VOLTAGE (V)
6.5
Figure 3. Regulated Output Voltage (floating) vs.
Input Voltage
4.30 0.80
4.25
4.20
4.15
4.10
4.05 VCC = 5 V
VBAT floating
4.00
−50
−25 0
25 50 75 100
TA, AMBIENT TEMPERATURE (°C)
Figure 4. Regulated Output Voltage vs.
Temperature
125
0.78
0.76
0.74
0.72
VBAT = 3.7 V
0.70
4.5
5.0
5.5 6.0
VCC, INPUT VOLTAGE (V)
Figure 5. ISEL Voltage vs. Input Voltage
6.5
3.00
2.95
2.90
VBAT floating
RISEL = 270 k
IV2P8 = 0
2.85
2.80
2.75
2.70
4.5
5.0 5.5 6.0
VCC, INPUT VOLTAGE (V)
Figure 6. V2P8 Voltage vs. Input Voltage
6.5
http://onsemi.com
5
5 Page 
NCP1835B
APPLICATION INFORMATION
Input and Output Capacitor Selection
A 4.7 mF or higher value ceramic capacitor is
recommended for the input bypass capacitor. For the output
capacitor, when there is no battery inserted and the
NCP1835B is used as an LDO with 4.2 V or 4.242 V output
voltage, a 4.7 mF or higher value tantalum capacitor is
recommended for stability. With the battery attached, the
output capacitor can be any type with the value higher than
0.1 mF.
CTIME Selection for Programming Charge Time
The NCP1835B offers an end−of−charge timeout timer
to prevent the battery from continuously charging which
can cause premature aging or safety issues. The timing
capacitor between TIMER pin and ground, CTIME, sets the
end−of−charge time, TIMEOUT, and the pre−charge
timeout. This capacitor is required for proper device
operation.
The internal oscillator charges CTIME to 1.2 V and then
discharges it to 0.6 V with 6 mA current in one period.
Therefore, the period of the oscillator is:
TOSC + 2
CTIME
IC
dVc + 0.2
106
CTIME (sec)
(eq. 1)
A 22−binary counter counts every oscillator period until
it reaches the maximum number corresponding to
end−of−charge time, TIMEOUT.
TIMEOUT + 222
TOSC + 14
CTIME
1 nF
(minute)
(eq. 2)
The NCP1835B will terminate charging and give a
timeout signal if the battery has not completed charging
within the TIMEOUT period. The timeout signal then
forces the FAULT pin low.
The following Table 2 shows the desired TIMEOUT vs.
CTIME sizes. The CTIME is required for proper device
operation.
Table 2. TIMEOUT vs. CTIME Size
CTIME (nF)
0.47
TIMEOUT (minute)
6.6
1 14
5.6 78
8.2 115
10 140
15 210
Thermal Considerations
www.DataSheet4U.com
The NCP1835B is housed in a thermally enhanced
3x3 mm DFN package. In order to deliver the maximum
power dissipation under all conditions, it is very important
that the user solders exposed metal pad under the package
to the ground copper area and then connect this area to a
ground plane through thermal vias. This can greatly reduce
the thermal impedance of the device and further enhance
its power dissipation capability and thus its output current
capability.
Charging with Constant Voltage Adapters or Current
Limited Adapters
The NCP1835B can be powered from two types of
regulated adapters: a traditional constant voltage type or a
current limited type. Figure 16 illustrates the operation of
the linear charger powered with a standard constant voltage
adapter. The power dissipation in the linear charger is:
Pdis + (VCC * VBAT) ICHG
(eq. 3)
The maximum power dissipation P1 happens at the
beginning of a full current charge, since this is the point that
the power supply and the battery voltage have the largest
difference. As the battery voltage rises during charging, the
power dissipation drops. After entering the constant
voltage mode, the power dissipation drops further due to
the decreasing charge current. The maximum power that
the linear charger can dissipate is dependent on the thermal
resistance of the device. In case the device can not handle
the maximum power P1, the thermal foldback loop reduces
the charge current which limits the power dissipation to the
sustained level P2. Figure 16 shows this.
Using the adapter’s current limit can provide better
thermal performance than the above example. A current
limited adapter operates as a constant voltage adapter
before the charge current reaches the current limit. ILIM
must be less than the programmed full charge current
IFCHG. Once the current limit is reached, the adapter will
source the current limit ILIM while its output voltage will
drop to follow the battery voltage. If the application uses
the adapter to power its systems while the battery is being
charged, this drooping voltage can be an issue.
The worst case power dissipation with a current limited
adapter occurs at the beginning of the constant voltage
mode, which is shown at point P3 in Figure 17. If P3 is
higher than P2, the maximum power dissipation that the
charger can handle, then the thermal foldback function will
be activated.
33 462
56 784
http://onsemi.com
11
11 Page | ||
| Páginas | Total 14 Páginas | |
| PDF Descargar | [ Datasheet NCP1835B.PDF ] | |
Hoja de datos destacado
| Número de pieza | Descripción | Fabricantes |
| NCP1835 | Integrated Li-Ion Charger | ON Semiconductor |
| NCP1835B | Integrated Li-Ion Charger | ON Semiconductor |
| Número de pieza | Descripción | Fabricantes |
| SLA6805M | High Voltage 3 phase Motor Driver IC. |
Sanken |
| SDC1742 | 12- and 14-Bit Hybrid Synchro / Resolver-to-Digital Converters. |
Analog Devices |
|
DataSheet.es es una pagina web que funciona como un repositorio de manuales o hoja de datos de muchos de los productos más populares, |
| DataSheet.es | 2020 | Privacy Policy | Contacto | Buscar |
