
|
|
PDF M24256-A Data sheet ( Hoja de datos )
| Número de pieza | M24256-A | |
| Descripción | 256 Kbit Serial I C Bus EEPROM With Two Chip Enable Lines | |
| Fabricantes | STMicroelectronics | |
| Logotipo |  |
|
Hay una vista previa y un enlace de descarga de M24256-A (archivo pdf) en la parte inferior de esta página. Total 20 Páginas | ||
|
No Preview Available !
M24256-A
256 Kbit Serial I C Bus EEPROM
With Two Chip Enable Lines
PRELIMINARY DATA
s Compatible with I2C Extended Addressing
s Two Wire I2C Serial Interface
Supports 400 kHz Protocol
s Single Supply Voltage:
– 4.5V to 5.5V for M24256-A
– 2.5V to 5.5V for M24256-AW
– 1.8V to 3.6V for M24256-AR
s 2 Chip Enable Inputs: up to four memories can
be connected to the same I2C bus
s Hardware Write Control
s BYTE and PAGE WRITE (up to 64 Bytes)
s RANDOM and SEQUENTIAL READ Modes
s Self-Timed Programming Cycle
s Automatic Address Incrementing
s Enhanced ESD/Latch-Up Behavior
s More than 100,000 Erase/Write Cycles
s More than 40 Year Data Retention
DESCRIPTION
These I2C-compatible electrically erasable pro-
grammable memory (EEPROM) devices are orga-
nized as 32Kx8 bits, and operate down to 2.5 V
(for the M24256-AW), and down to 1.8 V (for the
M24256-AR).
The M24256-A is available in Plastic Dual-in-Line,
Plastic Small Outline and Thin Shrink Small Out-
line packages. The M24256-A is also available in
a chip-scale (SBGA) package.
Table 1. Signal Names
E0, E1
Chip Enable
SDA
Serial Data
SCL
Serial Clock
WC Write Control
VCC
VSS
Supply Voltage
Ground
8
1
PSDIP8 (BN)
0.25 mm frame
8
1
SO8 (MN)
150 mil width
14
1
TSSOP14 (DL)
169 mil width
SBGA
SBGA7 (EA)
140 x 90 mil
8
1
SO8 (MW)
200 mil width
Figure 1. Logic Diagram
VCC
2
E0-E1
SCL
WC
M24256-A
SDA
VSS
AI02271C
April 2000
This is preliminary information on a new product now in development or undergoing evaluation. Details are subject to change without notice.
1/20
1 page 
Table 3. Device Select Code 1
Device Type Identifier
b7 b6 b5
Device Select Code
1
0
Note: 1. The most significant bit, b7, is sent first.
1
b4
0
M24256-A
Chip Enable
b3 b2 b1
0 E1 E0
RW
b0
RW
Acknowledge Bit (ACK)
An acknowledge signal is used to indicate a suc-
cessful byte transfer. The bus transmitter, whether
it be master or slave, releases the SDA bus after
sending eight bits of data. During the 9th clock
pulse period, the receiver pulls the SDA bus low to
acknowledge the receipt of the eight data bits.
Data Input
During data input, the memory device samples the
SDA bus signal on the rising edge of the clock,
SCL. For correct device operation, the SDA signal
must be stable during the clock low-to-high transi-
tion, and the data must change only when the SCL
line is low.
Memory Addressing
To start communication between the bus master
and the slave memory, the master must initiate a
START condition. Following this, the master sends
the 8-bit byte, shown in Table 3, on the SDA bus
line (most significant bit first). This consists of the
7-bit Device Select Code, and the 1-bit Read/Write
Designator (RW). The Device Select Code is fur-
ther subdivided into: a 4-bit Device Type Identifier,
and a 3-bit Chip Enable “Address” (0, E1, E0).
To address the memory array, the 4-bit Device
Type Identifier is 1010b.
Up to four memory devices can be connected on a
single I2C bus. Each one is given a unique 2-bit
code on its Chip Enable inputs. When the Device
Select Code is received on the SDA bus, the mem-
ory only responds if the Chip Select Code is the
same as the pattern applied to its Chip Enable
pins.
Table 4. Most Significant Byte
b15 b14 b13 b12 b11 b10 b9 b8
Note: 1. b15 is treated as Don’t Care on the M24256-A series.
Table 5. Least Significant Byte
b7 b6 b5 b4 b3 b2 b1 b0
The 8th bit is the RW bit. This is set to ‘1’ for read
and ‘0’ for write operations. If a match occurs on
the Device Select Code, the corresponding mem-
ory gives an acknowledgment on the SDA bus dur-
ing the 9th bit time. If the memory does not match
the Device Select Code, it deselects itself from the
bus, and goes into stand-by mode.
There are two modes both for read and write.
These are summarized in Table 6 and described
later. A communication between the master and
the slave is ended with a STOP condition.
Each data byte in the memory has a 16-bit (two
byte wide) address. The Most Significant Byte (Ta-
ble 4) is sent first, followed by the Least significant
Byte (Table 5). Bits b15 to b0 form the address of
the byte in memory. Bit b15 is treated as Don’t
Care bits on the M24256-A memory.
Write Operations
Following a START condition the master sends a
Device Select Code with the RW bit set to ’0’, as
shown in Table 6. The memory acknowledges this,
and waits for two address bytes. The memory re-
Table 6. Operating Modes
Mode
RW bit
Current Address Read
1
Random Address Read
0
1
Sequential Read
1
Byte Write
0
Page Write
Note: 1. X = VIH or VIL.
0
WC 1
X
X
X
X
VIL
VIL
Data Bytes
Initial Sequence
1 START, Device Select, RW = 1
START, Device Select, RW = 0, Address
1
reSTART, Device Select, RW = 1
≥ 1 Similar to Current or Random Address Read
1 START, Device Select, RW = 0
≤ 64 START, Device Select, RW = 0
5/20
5 Page 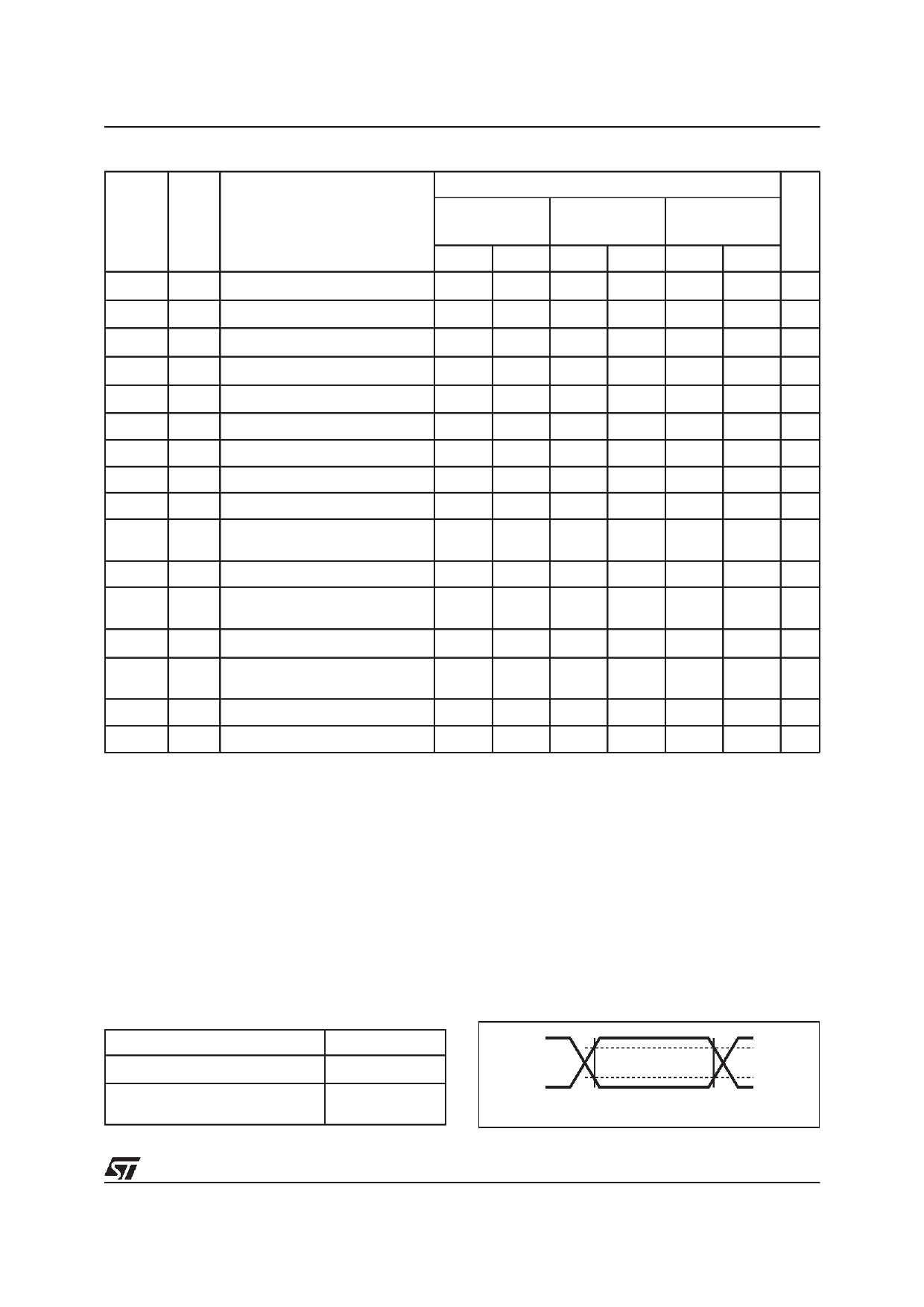
M24256-A
Table 9. AC Characteristics
M24256-A
Symbol Alt.
Parameter
VCC=4.5 to 5.5 V
TA=–40 to 85°C
VCC=2.5 to 5.5 V
TA=–40 to 85°C
VCC=1.8 to 3.6 V
TA=–20 to 85°C4
Unit
Min Max Min Max Min Max
tCH1CH2
tR Clock Rise Time
300 300 1000 ns
tCL1CL2
tF Clock Fall Time
300 300 300 ns
tDH1DH2 2 tR SDA Rise Time
20 300 20 300 20 1000 ns
tDL1DL2 2
tCHDX 1
tCHCL
tF SDA Fall Time
tSU:STA Clock High to Input Transition
tHIGH Clock Pulse Width High
20 300 20 300 20 300 ns
600
600
4700
ns
600
600
4000
ns
tDLCL
tCLDX
tHD:STA Input Low to Clock Low (START)
tHD:DAT Clock Low to Input Transition
600
0
600
4000
ns
0 0 µs
tCLCH tLOW Clock Pulse Width Low
1.3
1.3
4.7 µs
t DXCX
tSU:DAT
Input Transition to Clock
Transition
100
100
250 ns
tCHDH tSU:STO Clock High to Input High (STOP)
600
600
4000
ns
tDHDL
tBUF
Input High to Input Low (Bus
Free)
1.3
1.3
4.7 µs
tCLQV 3
tAA Clock Low to Data Out Valid
200 900 200 900 200 3500 ns
tCLQX
tDH
Data Out Hold Time After Clock
Low
200
200
200 ns
fC fSCL Clock Frequency
400 400 100 kHz
tW tWR Write Time
10 10 10 ms
Note: 1. For a reSTART condition, or following a write cycle.
2. Sampled only, not 100% tested.
3. To avoid spurious STAR T and STOP conditions, a minimum delay is placed between SCL=1 and the falling or rising edge of SDA.
4. This is preliminary data.
Table 10. AC Measurement Conditions
Input Rise and Fall Times
≤ 50 ns
Input Pulse Voltages
0.2VCC to 0.8VCC
Input and Output Timing
Reference Voltages
0.3VCC to 0.7VCC
Figure 9. AC Testing Input Output Waveforms
0.8VCC
0.7VCC
0.2VCC
0.3VCC
AI00825
11/20
11 Page | ||
| Páginas | Total 20 Páginas | |
| PDF Descargar | [ Datasheet M24256-A.PDF ] | |
Hoja de datos destacado
| Número de pieza | Descripción | Fabricantes |
| M24256-A | 256 Kbit Serial I C Bus EEPROM With Two Chip Enable Lines | STMicroelectronics |
| M24256-A125 | Automotive 256-Kbit serial I2C bus EEPROM | STMicroelectronics |
| M24256-B | 256/128 Kbit Serial I C Bus EEPROM With Three Chip Enable Lines | STMicroelectronics |
| M24256-BF | 256-Kbit serial I2C bus EEPROM | STMicroelectronics |
| Número de pieza | Descripción | Fabricantes |
| SLA6805M | High Voltage 3 phase Motor Driver IC. |
Sanken |
| SDC1742 | 12- and 14-Bit Hybrid Synchro / Resolver-to-Digital Converters. |
Analog Devices |
|
DataSheet.es es una pagina web que funciona como un repositorio de manuales o hoja de datos de muchos de los productos más populares, |
| DataSheet.es | 2020 | Privacy Policy | Contacto | Buscar |
